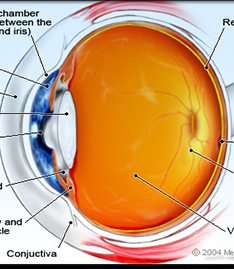
ANATOMY OF THE EYE
1. Cornea
The cornea is sometimes referred to as the “window of the eye.” It provides most of the focusing power when light enters your eye. The cornea is composed of 5 layers of tissue. The outer layer (the epithelium) is the eye’s protective layer. This layer is made up of highly regenerative cells that have the ability to grow back within 3 days, and therefore, allow for fast healing of superficial injuries. Most of the inner layers provide strength to the eye. The laser vision correction procedure is performed on this part of the eye.
2. Lens
The lens is the clear structure located behind the pupil. Its primary function is to provide fine-tuning for focusing and reading. The lens performs this function by altering its shape to become thinner or thicker as necessary. Between the ages of 40 and 50, the lens becomes less flexible and presbyopia sets in. As people reach their 60’s or 70’s, the lens sometimes becomes cloudy and hard (cataract formation), preventing light from entering the eye.
3. Pupil
The pupil is the ‘black circle’ that you see in people’s eyes. The primary function of the pupil is to control the amount of light entering the eye. When you are in a bright environment, the pupil becomes smaller to allow less light through. When it is dark, the pupil expands to allow more light to reach the back of the eye.
4. Iris
This is the colored part you see in people’s eyes (i.e. blue/green/brown/hazel). The primary function of the iris is to control the size of the pupil. This is achieved through contraction or expansion of the muscles of the iris.
5. Vitreous Body
This is the clear ‘gel like’ substance located inside the eye’s cavity. Its purpose is to provide a spherical shape to the eye. The vitreous may develop small clumps known as ‘floaters,’ which are more common in nearsighted people than in the rest of the population.
6. Optic Nerve
The optic nerve carries images from the retina to the brain.
7. Retina
The retina consists of fine nerve tissue which lines the inside wall of the eyes and acts like the film in a camera. Its primary function is to transmit images to the brain. When your vision is perfect, the light rays coming into your eye focus precisely on this part of the eye.
8.Sclera
This is the ‘white part’ that we see in people’s eyes. The sclera’s purpose is to provide structure, strength and protection to the eye.
We Exist for Your Healthy Eyesight
We Treat Patients like Family
Friendly and Knowledgeable Team
We are Pioneers
State of the Art Eye Hospital Advanced Technology
We are Committed to Welfare and Eye Health of Communities
Eye Health
Better Eye Care is Our Mission
Request Appointments.
For Lasik Surgery
Contact Following Numbers
Mr. Anand Agrawal
Mr. Balram
Mr. Gopal Badole
Dr. P.S. Hardia Advance Eye Surgery and Research Institute, Bypass Chouraha, A B Road, Opp Papaya Tree Hotel, Rau, Indore, Madhya Pradesh 453331